Understanding the "TEN Test" and Its Compatibility with Inventis Audiometers
The "TEN Test" (Threshold Equalizing Noise) was developed to identify dead regions in the cochlea, specifically targeting the inner hair cells (for additional information, refer to Brian Moore's 2004 Ear and Hearing). Recognizing these regions proves valuable in both selecting cochlear implant candidates and appropriately fitting hearing aids.
Before conducting the TEN test, the examiner must first determine the patient's hearing thresholds using earphones. After establishing these thresholds, initiate the TEN test. The suggested configuration involves presenting the pure tone stimulus in channel 1 and the TEN noise in channel 2, both routed to the same ear (ipsilaterally).
Choose the frequency for the test, ranging between 500 Hz and 4000 Hz. Adjust the intensity of the TEN noise based on the initial hearing threshold. For hearing thresholds equal to or below 60 dB HL, set the TEN stimuli at 70 dB. For thresholds exceeding 60 dB, present the TEN noise at 10 dB above the hearing thresholds, up to 90 dB. Re-establish audiometric hearing thresholds in 2 dB increments using the Hughson-Westlake method. Save this threshold for interpretation. Repeat the process in areas where dead regions are expected.
Interpretation involves verifying two criteria:
- Is the masked threshold greater than or equal to 10 dB above the level of the TEN stimuli? (Proceed to criteria 2 if yes; the test is inconclusive if no.)
- Is the masked threshold greater than or equal to 10 dB above the non-masked threshold?
If both criteria are met, a dead region is present. If not, no dead regions are identified.
If the above is true dead region present. If the above is false then no dead regions is identified.
The TEN test can be conducted with various Inventis devices, such as Harp Plus, Piano Basic, and Piano Plus. Sounds are presented either with supra-aural headphones or insert earphones. The test material is recorded on two channels: channel 1 for the stimulus and channel 2 for noise.
To perform the test, it is essential to have previously assessed the patient's pure-tone threshold levels between 500 and 4000 Hz.
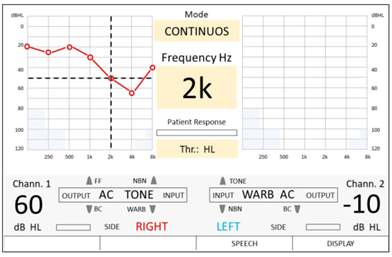
Afterwards, the user can access the TEN test screen from the audiometer main menu and see the pure tone audiogram displayed on the background of the graph.
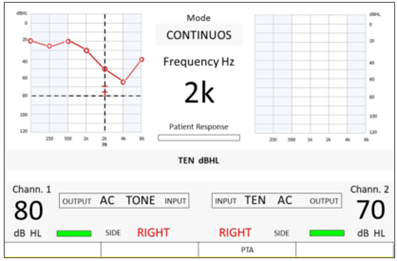
From the dedicated screen for the TEN test, users have the ability to configure the stimulated side and adjust the intensities for both the stimuli and noise. Throughout the TEN test, users can opt for either a continuous or pulsed stimulus and can activate tracking or lock options. The audiogram prominently features stored masked thresholds represented by a "T" symbol. The associated masking levels, measured in dB HL, are conveniently displayed in the lower section of the graph.
* The content has undergone a slight revision by the Academia editorial team.


 Go to the top
Go to the top

 International - English
International - English Italia - Italiano
Italia - Italiano France - Français
France - Français USA - English
USA - English